Definition
Price Elasticity of Supply measures the proportionate change
in quantity supplied in respect of a proportionate change in price.
What are the factors which affect the
potential supply of a good?
- The formula is the same one which we have come to know from PRICE ELASTICITY OF
DEMAND.
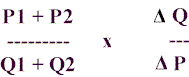
where P1 is the first price, P2 is the second price, Q1 is the first quantity supplied,
and Q2 is the second quantity supplied.
The 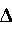 is pronounced "delta" (Greek) and it means "change in". is pronounced "delta" (Greek) and it means "change in".
The major difference here is that the sign will be positive,
almost invariably. Given that the higher the price, the greater the quantity which the
producers are willing to supply, the sign when we work out our formula
will be positive. An increase in price (plus) brings
about an increase in supply (plus).
- A plus by a plus will give us a plus.
Conversely, a fall in price expectations will lead the supplier to reduce the supply of
those goods - a minus by a minus will also give a plus.
|
Any supply curve which goes through the origin
point of a chart will have unitary elasticity of supply along
its entire slope, on the assumption that the supply curve is a straight line. This is true
irrespective of the angle of the slope.
IF A SUPPLY CURVE GOES THROUGH THE ORIGIN,
IT HAS UNITARY ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY. |
Return to Top
What are the factors which affect the potential supply of a good?
1. Perishability of the Goods:
If goods are likely to perish, or become obsolete, then the elasticity of supply will
become quite high.
Any slight movement in price will tend to see a major change in quantity supplied,
because suppliers do not wish to be left with the costs of storing obsolete or otherwise
unsaleable goods.
2. Production Costs:
We have always assumed that the higher the price, the more the supplier would be
willing to put onto the market.
- If the supplier can do this Elasticity of Supply (PES) would be elastic.
However, this is only true if increasing supply does not incur extra costs which would
cancel out the extra revenue to be got from the extra sales.
- If the supplier had to purchase an extra machine in order to produce and sell more, and
the new machine is not being fully utilised, it is quite possible that the average cost of
production will rise. This increased cost of production may be not fully recovered from
the revenue from extra sales.
3. Time Period:
If we talk about demand, the consumer is sovereign.
If price goes up, the consumer can make an immediate decision to buy or not to buy.
- However, there is a time-lag when we discuss
supply.
The decision as to how many fresh turkeys will be put onto the market at Christmas time
is taken sometime in August/September. No matter what happens to the price of turkeys in
the week before Christmas, a supplier cannot vary output.
- The supply of goods which have a relatively long time-lag would be said
to be inelastic.
Return to Top
|
2006
MasterIT.ie - Computer Consultancy, Website
Development, Educational Software |
|